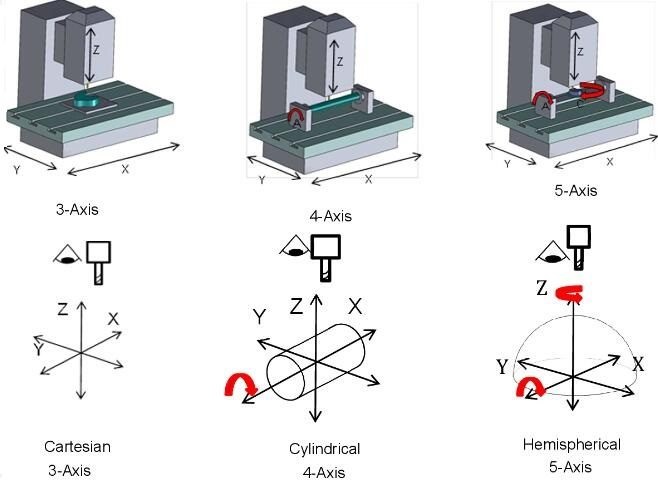
CNC routers have revolutionized manufacturing by offering highly precise, automated control over cutting, milling, and drilling operations. A key component of these machines is their axes, which determine how they move and interact with materials. These routers come in different axes to improve their functionality for various applications.
Understanding the number of axes a CNC router uses—whether 3, 4, or 5—can greatly impact the quality, efficiency, and type of projects that can be completed. We’ve put together this article to help you understand 3 Axis vs 4 Axis vs 5 Axis CNC Router differences. This way, you’ll know how to choose the right CNC routing type for your manufacturing needs.
What Does Axes Mean in CNC Service?
In CNC machining, the term “axes” refers to the directional movements that the machine is capable of performing. Each axis corresponds to a plane along which the tool can move, determining the direction and complexity of cuts.
Axes in CNC service
The most basic CNC machine works on three axes: the X-axis (horizontal movement), Y-axis (vertical movement), and Z-axis (depth movement). Together, these allow the machine to perform a wide range of cutting and shaping tasks. However, adding more axes, such as the rotational A or B axis in 4-axis and 5-axis machines. This enhances the machine’s versatility, enabling more intricate designs and faster production times.
Different numbers of axes also affect the machine’s precision, efficiency, and ability to work on complex parts without manual repositioning of the material. This makes multi-axis CNC routers superior custom CNC solutions for many industries requiring top-level accuracy and detail.
What Is a 3-Axis CNC Router?
A 3-axis CNC router is the most commonly used CNC machine for cutting, drilling, and milling flat materials. It moves the cutting tool in three directions: the X, Y, and Z axes. This allows it to cut along the horizontal, vertical, and depth planes, respectively.
3-axis CNC router
Features:
- Ideal for simple projects on flat surfaces.
- Used widely in industries like woodworking, signage, and basic machining.
- Easy to operate, with a relatively lower learning curve.
Pros:
- Cost-effective and more accessible to small businesses or hobbyists.
- Simpler operation, requiring less technical expertise.
- Best for basic cuts on flat materials.
- Quicker setup time due to reduced complexity.
- Fewer maintenance requirements compared to multi-axis machines.
Cons:
- Limited in handling complex designs with intricate cuts.
- Requires manual repositioning of the material for detailed projects.
What Is a 4-Axis CNC Router?
A 4-axis CNC router adds rotational movement to the cutting tool by incorporating the A-axis, which allows the machine to rotate the material around the X-axis. This extra axis provides the ability to work on cylindrical or curved surfaces without manual repositioning.
4-axis CNC router
Features:
- The ability to work on round objects, such as pipes or beams.
- It can handle more complex shapes than a 3-axis router.
- Enhanced precision due to the additional rotational axis.
Pros:
- Ideal for projects involving cylindrical parts or surface engraving on curved materials.
- Can perform cuts on multiple sides without manual repositioning.
- Increased flexibility for medium-complexity projects.
- Faster production times on curved materials.
- Less human intervention, improving consistency in production.
- Supports indexing for accurate positioning of the workpiece.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to 3-axis machines.
- Requires more programming knowledge and operational expertise.
What Is a 5-Axis CNC Router?
A 5-axis CNC router introduces two additional rotational axes: typically the A-axis and B-axis, allowing the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction. This machine type is commonly used in industries requiring precision machining of complex shapes, such as aerospace or automotive components.
5-axis CNC router
Features:
- Full rotation of the cutting tool and the material, allowing the most intricate designs.
- The ability to machine parts with complex geometries without needing to reposition the material.
- Extremely high precision and reduced production time for complex parts.
Pros:
- Handles the most complex cuts and designs in a single operation.
- Capable of creating components that would be impossible with 3-axis or 4-axis routers.
- Reduces the need for multiple setups, saving time and improving efficiency.
- Eliminates manual repositioning, reducing errors.
- Perfect for high-precision industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Cons:
- Very high initial investment.
- Requires highly skilled operators and advanced programming knowledge.
3 Axis vs 4 Axis vs 5 Axis CNC Router: Main Differences
When choosing between a 3 vs 4 vs 5-axis CNC router, understanding the fundamental differences is crucial. Here’s a comparison based on the most important factors:
Number of Motion Axes
The most fundamental difference between 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC routers is the number of motion axes they provide. A 3-axis router operates along the X, Y, and Z axes, meaning it can move a cutting tool up and down, left and right, and back and forth. This allows for basic milling, drilling, and cutting tasks. However, it cannot handle more complex shapes. The 4-axis router adds a rotational axis, which enables the machine to rotate the workpiece or the cutting tool around the X or Y axis. This additional motion makes working on cylindrical or irregularly shaped objects possible. It also allows for more advanced designs.
3, 4, and 5-axis CNC router comparison
A 5-axis CNC router takes it a step further by incorporating two rotational axes. It enables the cutting tool or workpiece to rotate around both the X and Y axes. This allows for highly intricate designs and the ability to access all sides of a part without needing to reposition it manually.
Machine Bed
In a 3-axis router, the bed is usually static, meaning the workpiece remains fixed in place while the cutting tool moves across it. This simple setup is ideal for smaller, less complex projects. In contrast, a 4-axis router typically requires a rotary table or additional fixtures to support the rotational movement of the workpiece, making the bed more versatile and slightly more complex.
A 5 axis CNC router often has a tilting or rotating bed that works in tandem with the cutting tool’s rotational axes, offering unparalleled flexibility. This allows for machining at various angles and reduces the need for manual intervention. However, it also increases the complexity and cost of the machine bed.
Working Methods
The working methods of these machines are closely tied to their number of axes. A 3 axis CNC router performs linear machining, where the cutting tool engages the workpiece in straight lines along the X, Y, and Z axes. This is effective for simple designs but limits the machine’s versatility.
The 4-axis router enhances these working methods by adding rotational motion, allowing the machine to carve more intricate shapes and work with curved surfaces. This feature is particularly useful in industries like woodworking. A 5-axis router offers the most advanced working methods. It allows for simultaneous movement across all five axes. This capability enables continuous machining of complex geometries without the need to stop and reposition the workpiece. Thus, many machinists use it for aerospace, automotive, and other high-precision industries.
Processing Capacity
A 3-axis CNC router is the most basic and is suitable for low to medium-complexity tasks. It handles flat materials like sheets of metal, plastic, or wood but struggles with parts that require access from multiple angles. A 4-axis router offers increased processing capacity by enabling the cutting tool to engage with the workpiece from additional angles. This allows for more efficient machining of 3D shapes and reduces the need for manual repositioning to ensure high-speed CNC routing.
The 5-axis router offers the highest processing capacity of all, allowing for the creation of highly intricate, multi-dimensional parts. It is designed for high-precision manufacturing and is capable of producing complex geometries with minimal operator intervention.
Structure and Complexity
The structural complexity of CNC routers increases with the number of axes. A 3-axis router has a relatively simple structure. Thus, it is easier to operate and maintain. It’s typically the best choice for beginners or businesses that don’t require advanced capabilities. 4 axis CNC routing adds complexity by introducing a rotational axis. It requires additional components like a rotary table or more advanced software to control the machine. This makes the setup and operation slightly more complex but still manageable for most operators.
Conversely, a 5-axis CNC router is highly complex in terms of structure and operation. It requires sophisticated software, more intricate components, and higher expertise to run efficiently. As a result, it is better suited for advanced users or industries that demand high precision.
Cooling Method
CNC routers generate heat during operation, and the cooling method used can differ based on the number of axes. A 3-axis CNC router typically uses air cooling or simple water cooling systems. This is because the machine’s demands are lower. Machinists use more advanced cooling systems for 4-axis machines, especially when working with tougher materials or longer production runs. These systems include high-pressure water jets or oil-based systems used to prevent overheating.
A 5-axis CNC router tends to require sophisticated cooling methods like integrated cooling channels, oil-mist systems, or even refrigerated cooling. These methods help maintain the integrity of the workpiece and ensure dimensional accuracy.
Scope of Applications
The applications of these machines vary widely. A 3-axis CNC router is ideal for basic cutting, drilling, and milling tasks and is commonly used in industries like signage, cabinetry, and hobbyist projects. A 4-axis router extends the range of applications to include more detailed woodwork, mold making, and the production of cylindrical objects.
The 5-axis router has the broadest scope of applications, ranging from aerospace and automotive industries to complex medical device manufacturing. It is well-suited for creating parts with complex geometries that require precision from multiple angles.
Cost
A 3-axis CNC router is the most affordable, making it attractive for small businesses or those with limited budgets. It provides excellent value for simple tasks but lacks the versatility of more advanced machines. A 4 axis CNC router is more expensive due to its additional axis and the need for more complex components. However, it offers greater flexibility for businesses looking to expand their capabilities.
A 5-axis CNC router represents the highest investment in terms of both purchase price and operational costs. However, for industries that require high precision and efficiency, the investment pays off by reducing manual labor, improving production times, and enabling the creation of complex parts.
How to Choose Between 3, 4, and 5 Axis CNC Routers
When choosing the right CNC router for your needs, consider these factors:
Applications
The first consideration should be the intended application when selecting between a 3, 4, or 5-axis CNC router. For simple jobs like cutting flat sheets of material or performing basic drilling tasks, a 3-axis router is more than sufficient. However, if your projects require working with 3D shapes, curved surfaces, or cylindrical objects, a 4-axis machine will provide the additional functionality needed. On the other hand, a 5-axis router is essential if you work in industries requiring the highest level of precision and complexity, such as aerospace, medical devices, or high-end automotive parts.
Processing Requirements
A 3-axis CNC router is suitable for tasks that involve simple, two-dimensional processing, such as cutting or drilling flat surfaces. If your parts require more detailed processing, such as working on curved surfaces or creating intricate 3D designs, a 4-axis machine may be the better option. A 5-axis router is ideal for the most complex projects, where multiple angles and sides of a workpiece must be machined without repositioning. The more complex the processing requirements, the more likely you’ll need a machine with additional axes.
Equipment Compatibility
Consider how the chosen CNC router fits with your existing equipment. A 3-axis CNC router is often the most compatible with standard workshop setups, requiring minimal additional components. A 4-axis router might require the addition of a rotary table or specific fixtures to handle the fourth axis, which could necessitate some upgrades to your current setup. A 5-axis router, being highly advanced, often requires sophisticated software, more complex control systems, and possibly even dedicated workspaces. Evaluate your current equipment and the compatibility with the CNC router. This will help ensure a smooth transition and efficient operation.
Operations and Maintenance
A 3-axis CNC router is generally the easiest to operate. It is a good starting point for those new to CNC machining. Maintenance is also straightforward, as the machine has fewer moving parts and less complex components. A 4-axis router introduces more complexity in operation and maintenance. It requires additional controls for the fourth axis. A 5-axis CNC router is the most challenging to operate and maintain, with more intricate parts and more sophisticated software. However, for experienced users and advanced applications, the added complexity is often justified by the machine’s capabilities.
Budget
Budget constraints will heavily influence your decision when choosing CNC routers. A 3-axis CNC router is the most cost-effective option, offering good value for businesses that don’t need advanced functionality. A 4-axis router represents a middle ground. It provides additional versatility at a higher price point but still within reach for many small to medium-sized businesses. A 5-axis CNC router is the most expensive. It requires a significant investment in initial cost and ongoing operational expenses. However, the return on investment can be substantial if your business demands high precision and complex machining.
Comparison Table for 3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis CNC Routers
The table below summarizes the differences between 3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis CNC Routers to help you put it in better perspective.
| Feature | 3-Axis CNC Router | 4-Axis CNC Router | 5-Axis CNC Router |
| Number of Motion Axes | 3 (X, Y, Z) | 4 (X, Y, Z, A) | 5 (X, Y, Z, A, B) |
| Machine Bed | Simple flat bed | Flat bed with rotational capabilities | Complex, can handle intricate workpieces |
| Working Methods | Limited to basic 2D/3D work | Can cut multiple sides without repositioning | Handles complex geometries with precision |
| Processing Capacity | Basic | Moderate complexity | High complexity, intricate parts |
| Structure Complexity | Simple | Moderate | Complex |
| Cooling Method | Basic air/liquid cooling | Improved cooling for complex work | Advanced cooling for precision work |
| Applications | Woodworking, plastic, simple metal | Engraving, cylinder cutting | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices |
| Cost | Affordable | Moderate | High, for precision-driven industries |
3-Axis vs 4-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC Routers table of comparison
Conclusion
CNC routers play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, enabling businesses to produce parts with exceptional precision and efficiency. Understanding the differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis routers is key to choosing the best option for your specific project requirements. A 3-axis router is ideal for straightforward tasks, providing excellent performance for flat or simple designs. If your project involves more complex geometries that require machining on multiple sides without resetting the workpiece, a 4-axis router offers enhanced versatility. For the most demanding projects that require multi-angle custom CNC routing with precise control, the 5-axis router is the top choice.
Zintilon stands as your trusted manufacturing partner. We offer expert CNC routing services to meet any production challenge. Whether you need a 3-axis router for simple cuts or a 5-axis router for intricate designs, Zintilon’s team is ready to provide high-quality solutions. Contact us today to discuss your project needs and discover how we can help you achieve manufacturing excellence.
Read More: How VTScada Can Simplify Your Water Management Process